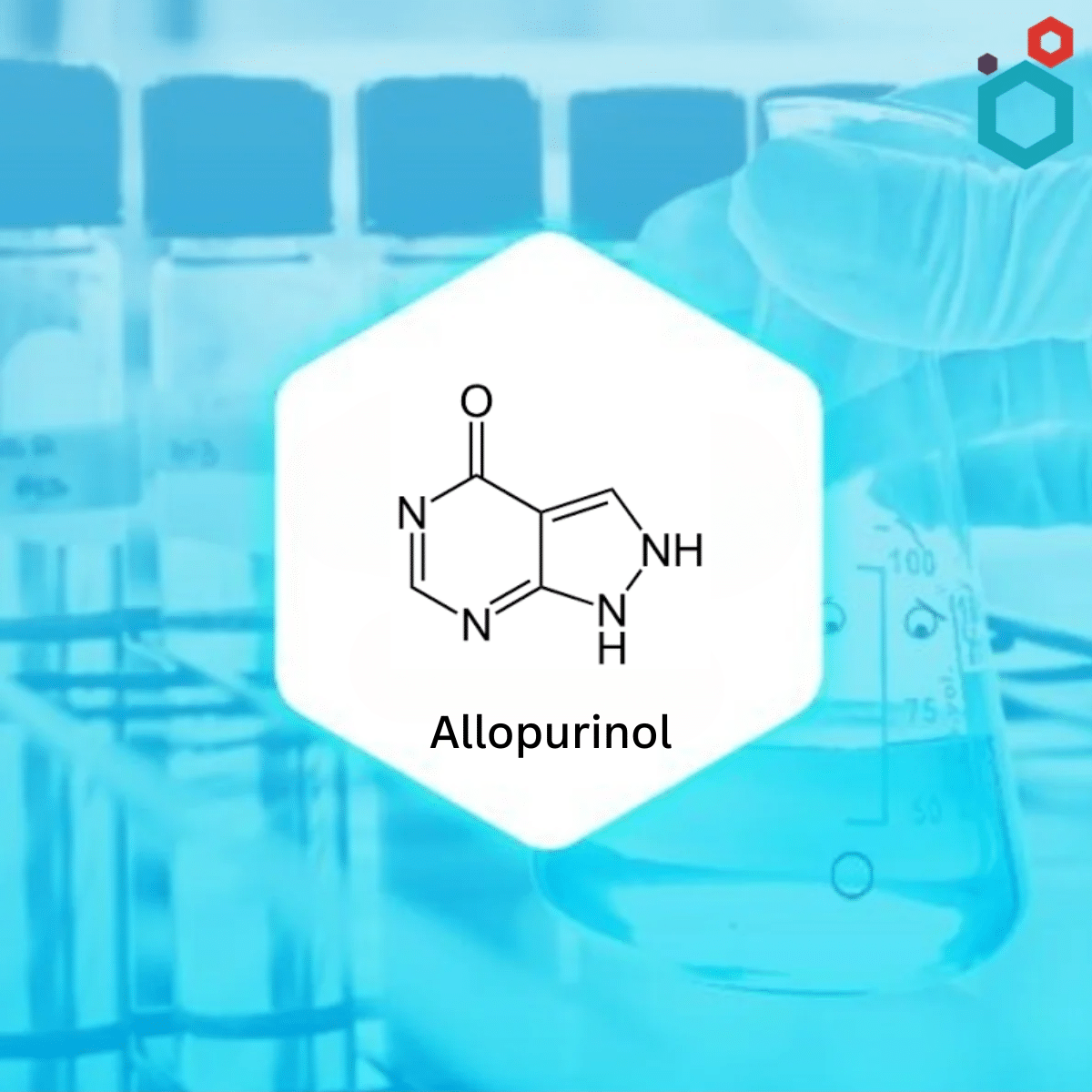
What is Allopurinol?
Allopurinol is a xanthine oxidase inhibitor used to treat hyperuricemia and gout. It reduces the production of uric acid by inhibiting xanthine oxidase, the enzyme responsible for converting hypoxanthine and xanthine into uric acid, thereby helping to lower serum and urinary uric acid levels.
Allopurinol, commonly sold under the brand names Aloprim and Zyloprim, was approved for medical use in the United States in 1966 and is available as a prescription medicine and is listed as an essential medicine by the World Health Organization.
| PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS | |
|---|---|
| Name of Product | Allopurinol EP/BP/USP |
| IUPAC Name | 1,5-dihydropyrazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidin-4-one |
| Synonyms | Allopurinolo, Allopurinolum, Alopurinol |
| CAS No | 315-30-0 |
| Molecular Formula | C5H4N4O |
| Molecular Weight | 136.11 g/mol |
Chemical Properties
| SR. No | Criteria | Limit/Specification |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Appearance (Form) | Powder |
| 2 | Appearance (Colour) | Fluffy White to off-White |
| 3 | Solubility | Sparingly soluble in water |
| 4 | Odor | Odorless |
| 5 | Taste | Slightly bitter |
Mechanism of action
Allopurinol undergoes metabolism in the liver, where it transforms into its pharmacologically active metabolite, oxypurinol. Both allopurinol and oxypurinol inhibit xanthine oxidase, the key enzyme in purine metabolism responsible for converting hypoxanthine → xanthine → uric acid. By inhibiting this pathway, allopurinol reduces uric acid formation and prevents gout attacks, uric acid kidney stones, and complications from hyperuricemia.
Allopurinol vs Other Gout Medications
Allopurinol vs Colchicine
- Allopurinol is a xanthine oxidase inhibitor, blocking the conversion of hypoxanthine and xanthine into uric acid, primarily used for long term management of hyperuricemia and gout, while Colchicine is an alkaloid extracted from the Colchicum autumnale plant. It inhibits microtubule polymerization, which interferes with neutrophil motility and activity. This reduces the inflammatory response to urate crystals in joints, controlling pain and swelling during acute attacks.
- Allopurinol prevents complications of hyperuricemia, while colchicine is used for acute gout flares to relieve pain and inflammation.
Allopurinol vs Febuxostat
- Allopurinol and Febuxostat are both xanthine oxidase inhibitors (XOIs). Allopurinol is a Purine analog that inhibits xanthine oxidase, while Febuxostat is a non-purine selective xanthine oxidase inhibitor.
- Allopurinol is a first-line treatment metabolized to oxypurinol and renally excreted, while febuxostat is metabolized in the liver and helps to manage chronic hyperuricemia in patients with gout when allopurinol is not tolerated or ineffective.
Uses
- Allopurinol helps to reduce serum uric acid levels to prevent recurrent gout attacks and tophi formation.
- It also lowers urinary uric acid levels and reduces the risk of uric acid kidney stones.
- Allopurinol is used in Tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) for patients with elevated uric acid due to chemotherapy or certain metabolic disorders.
Side Effects
Common Side Effects of Allopurinol include –
- Rash
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Drowsiness
Less common but other serious side effects include –
- Severe skin reactions, including Stevens–Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN)
- Bone marrow suppression, which may lead to anemia, leukopenia, or thrombocytopenia
- Hepatotoxicity (liver injury)
- Allopurinol Hypersensitivity Syndrome (AHS), a rare but potentially life-threatening reaction that may include rash, fever, liver dysfunction, and kidney impairment
FAQs
Q. What to avoid when taking Allopurinol?
Allopurinol helps lower uric acid levels in the blood, and during treatment, alcohol and high-purine foods should be avoided as they can raise uric acid levels and reduce its effectiveness.
Q. How does Allopurinol work?
Allopurinol works by reducing the production of uric acid in the body. It restricts the action of an enzyme called xanthine oxidase, which is responsible for converting substances called purines into uric acid and helping prevent gout attacks and reducing the risk of uric acid kidney stones.
Q. What is the most common side effect of Allopurinol?
Allopurinol is a safe and commonly prescribed generic medicine. Many people experience no side effects, while some may have mild stomach upset, drowsiness, or a skin rash.
Q. Why does Allopurinol worsen acute gout?
Allopurinol may sometimes worsen acute gout at the beginning of treatment. Because uric acid crystals in the blood decrease in size and can settle in the joints, causing a temporary flare, but this effect is usually temporary and improves with continued use of the medication.
Q. How long does Allopurinol take to work?
Allopurinol starts showing its effect within a few days, but it takes several weeks to lower uric acid levels and may take several months to years for the crystals around the joints to dissolve and be eliminated from the body.
Q. Is Allopurinol harmful to the kidneys?
Allopurinol is generally safe for the kidneys, and it helps to reduce urate crystal deposits and prevent kidney stone formation. However, in severe cases like AHS, it may cause kidney injury.
