What is Monobenzone?
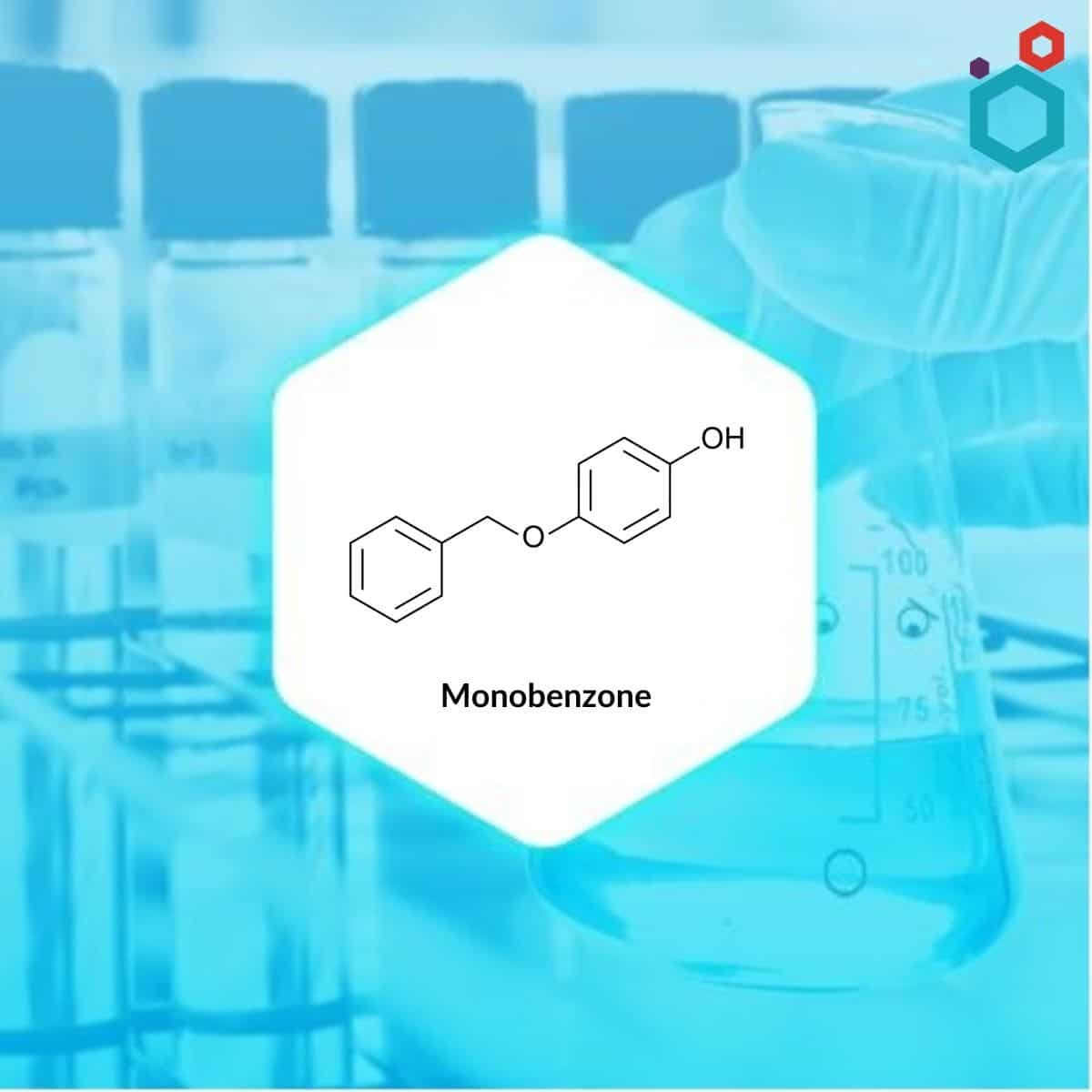
Monobenzone, also referred to as 4-(Benzyloxy)phenol, is the monobenzyl ether of hydroquinone. It occurs as white crystalline powder which is soluble in alcohol, benzene, and diethyl ether, and practically insoluble in water. It is used in topical medications for depigmentation to treat vitiligo.
| PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS | |
|---|---|
| Name of Product | Monobenzone USP |
| IUPAC Name | 4-phenylmethoxyphenol |
| Synonyms | 4-Benzyloxyphenol; Hydroquinone monobenzyl ether; Benoquin; Benzoquin; Monobenzyl hydroquinone |
| CAS No | 103-16-2 |
| Molecular Formula | C13H12O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 200.23 g/mol |
| Pubchem CID | 7638 |
Specifications
| SR. No | Criteria | Limit/Specification |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Appearance (Form) | Solid Crystalline Powder |
| 2 | Appearance (Color) | White |
| 3 | Solubility | Soluble in Alcohol, Ether and Benzene Insoluble in Water |
| 4 | Melting point | 110 - 113 °C |
| 5 | Residue on Ignition | NMT 0.5% |
| 7 | Loss on Drying (At 105°C for 3hr) | NMT 1.0% |
| 8 | Assay (On dried basis) | NLT 98.0% - NMT 102.0% |
Mechanism of action
- It acts as a melanin synthesis inhibitor by inhibiting the tyrosinase enzyme, which is responsible for melanin synthesis.
- It also induced the excretion of melanin from melanocytes.
Uses
- The primary use of Monobenzone is to treat Vitiligo, a disorder in which the skin loses its natural pigmentation (melanin), resulting in the formation of white patches. This condition occurs when pigment-producing cells die or cease to function.
- Monobenzone is a depigmenting agent that increases the elimination of melanin (pigment molecules) from skin cells. Depigmenting the darker skin surrounding vitiligo lesions helps achieve a more uniform complexion and appearance of the skin.
- The potential therapeutic application of monobenzone for melanoma is also under consideration.
Side effects
Some of the possible side effects associated with the use of monobenzone are –
- Mild skin irritation,
- Dryness or flaking of the skin
- Increased sensitivity of the skin
In some cases, monobenzone can make the treated skin more sensitive to sunlight.
FAQs
Q. Does monobenzone cause cancer?
Currently, there is no evidence of the potential carcinogenic effects of monobenzone.
Q. How long does monobenzone take to work?
Monobenzone will take almost 4 to 8 weeks to show its effects however it also varies from person to person, the extent of pigmentation, and the amount and frequency of its use.
Q. Is monobenzone permanent?
Monobenzone can lead to permanent depigmentation and damage melanocytes, the cells that produce melanin.
Q. What is the difference between mequinol and monobenzone?
Mequinol and monobenzone are both depigmenting agents used in dermatology. Both produce dramatic skin whitening but react very differently. Mequinol interferes with the enzymatic steps in melanin synthesis, thereby reducing the production of melanin in the skin. On the other hand, monobenzone irreversibly damages melanocytes (the cells responsible for producing melanin) resulting in permanent lightening of the treated skin.
Q. What are the side effects of monobenzone 20?
Monobenzone (20% w/w) has the same side effects as monobenzone. The only difference lies in its concentration.
Q. Can monobenzone cause Vitiligo?
Monobenzene can induce vitiligo-like depigmentation which is indistinguishable from vitiligo a condition of loss of pigment in patches of skin.
Q. Where can I buy monobenzone?
Macsen is the leading manufacturer and supplier of monobenzone. To buy monobenzone contact sales@macsenlab.com
Buy high-purity Monobenzone USP Powder from Macsen Laboratories. For buying, send us an inquiry-
