What is Benfotiamine?
Benfotiamine is a lipid-soluble synthetic derivative of thiamine (vitamin B₁) that helps enhance thiamine bioavailability and cellular uptake by converting the active form of B1 thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP). It helps correct dysfunctions in the biochemical pathways of diabetic retinopathy and nephropathy and is also widely utilized in nutritional, pharmaceutical, and research applications.
| PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS | |
|---|---|
| Name of Product | Benfotiamine |
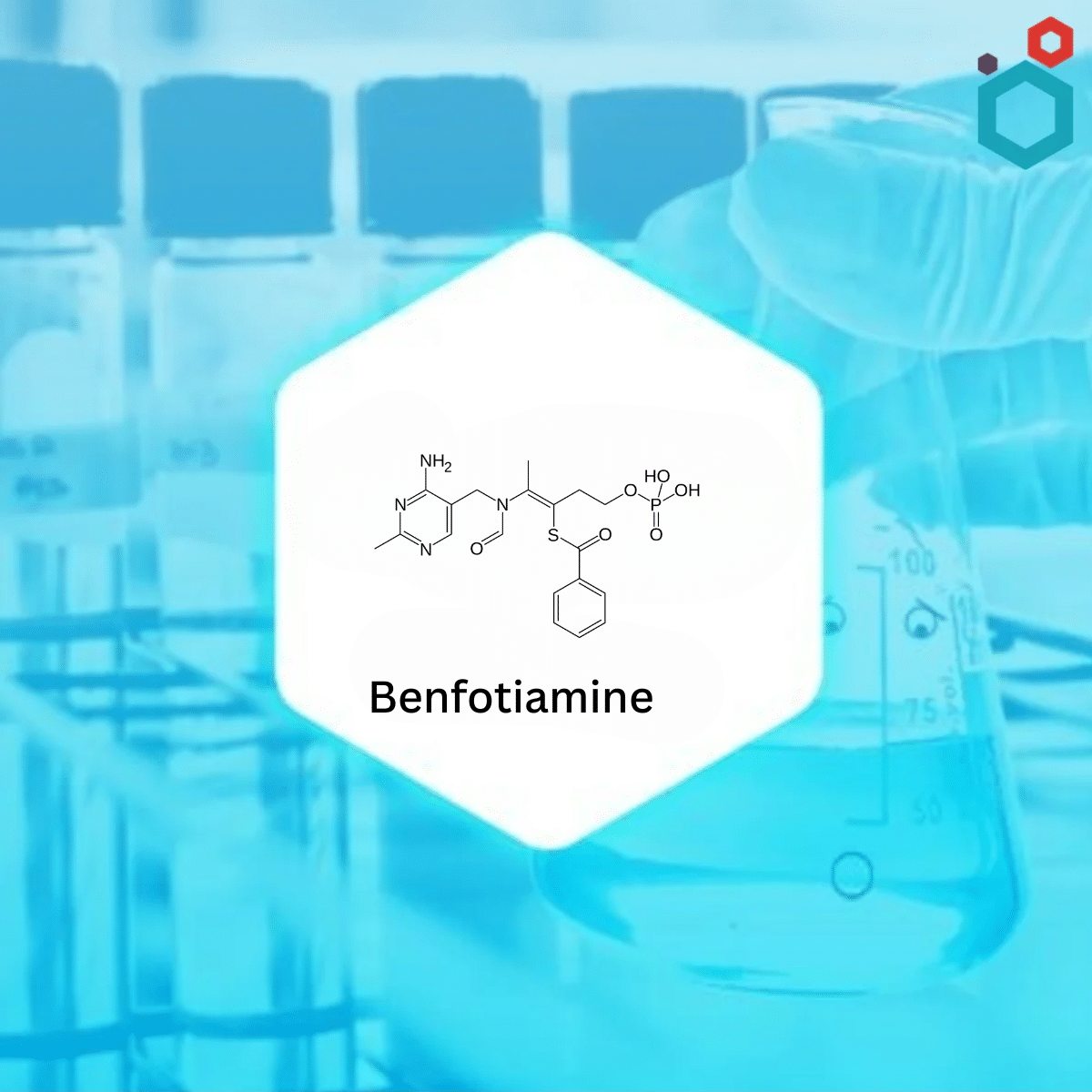
| IUPAC Name | S-[(Z)-2-[(4-amino-2-methylpyrimidin-5-yl)methyl-formylamino]-5-phosphonooxypent-2-en-3-yl] benzenecarbothioate |
| Synonyms | Benphothiamine, Biotamin, Benzoylthiamine monophosphate, Benfotiaminum
S-Benzoylthiamine O-monophosphate |
| CAS No | 22457-89-2 |
| Molecular Formula | C19H23N4O6PS |
| Molecular Weight | 466.4 g/mol |
| Pubchem CID | 3032771 |
Chemical Properties
| SR. No | Criteria | Limit/Specification |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Appearance (Form) | Crystalline powder |
| 2 | Appearance (Colour) | White to off-white |
| 3 | Solubility | Practically insoluble in water, slightly soluble in DMSO |
| 4 | Melting Point | 165 °C |
Benefits
- Benfotiamine is used to reduce neuropathic pain, numbness, and paresthesia caused by diabetic neuropathy.
- It is used in both the prevention and treatment of thiamine deficiency and is added to dietary supplements for the treatment of thiamine (vitamin B1) deficiency.
- Benfotiamine is also used in alcoholism-related thiamine deficiency.
- It helps lower the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease and arthritis and supports nerve health.
- It helps protect cells against oxidative stress and reduces inflammation in neural tissues.
- Benfotiamine also improves gut health, appetite, and digestion.
- It inhibits harmful metabolic pathways (AGEs, polyol pathway), thereby supporting protection against diabetic complications affecting nerves, kidneys, and blood vessels.
- It is used as a supportive supplement in metabolic syndrome and conditions associated with chronic hyperglycemia.
Side effects
Potential adverse reactions associated with benfotiamine include –
- Skin irritation and rashes
- Stomach Discomfort
- Nausea
- Facial Swelling
- Wheezing and coughing
- Increased sweating
FAQs
Q. How does Benfotiamine work?
Benfotiamine is a fat-soluble form of vitamin B1 that works by increasing intracellular levels of active thiamine and activating the enzyme transketolase. It also lowers the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and decreases oxidative stress and inflammation associated with chronic high blood sugar.
Q. Is Benfotiamine the same as vitamin B1 (Thiamine)?
Benfotiamine is a pro-vitamin form of thiamine that is converted into active thiamine inside the body and has higher bioavailability, while thiamine is a water-soluble vitamin (vitamin B₁) that has limited intestinal absorption and is rapidly excreted.
Q. What is Benfotiamine good for?
Benfotiamine is a synthetic derivative of vitamin B1, and it helps to treat thiamine deficiency, treat beriberi disease, and improve mental health.
Q. Does Benfotiamine raise blood pressure?
Benfotiamine is a fat-soluble form of vitamin B1 that primarily supports nerve function, glucose metabolism, and oxidative stress reduction, and it is safe, not known to raise blood pressure.
Q. Can you take Benfotiamine and thiamine together?
Benfotiamine is a more bioavailable, fat-soluble form of thiamine and can be taken in combination with thiamine to boost metabolic health, diabetes-related complications, and chronic deficiency states (e.g., alcoholism or malabsorption).
Q. How much benfotiamine should I take?
Benfotiamine intake depends on the intended use and clinical condition. Generally, for general supplementation and metabolic support, the dose is 150–300 mg per day; however, for diabetic complications, 300–600 mg per day is considered safe. It is advisable to consult a healthcare professional before use.
Q. What are the benefits of taking Benfotiamine and Alpha-Lipoic Acid together?
Alpha-Lipoic acid (ALA) is a potent antioxidant that helps in mitochondrial energy metabolism. It is combined with benfotiamine for the synergistic effects and improves nerve health, glucose metabolism, and metabolic stress-related conditions.
