What is Deferasirox?
Deferasirox is a member of the class of triazoles. It is an iron chelator that can be taken orally and is marketed under the brand names Exjade & Asunra (for injectable formulation) & Oleptiss (for tablet formulation). It was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in November 2005 for the treatment of chronic iron overload in patients receiving long term blood transfusions. It is also on the World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines.
| PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS | |
|---|---|
| Name of Product | Deferasirox |
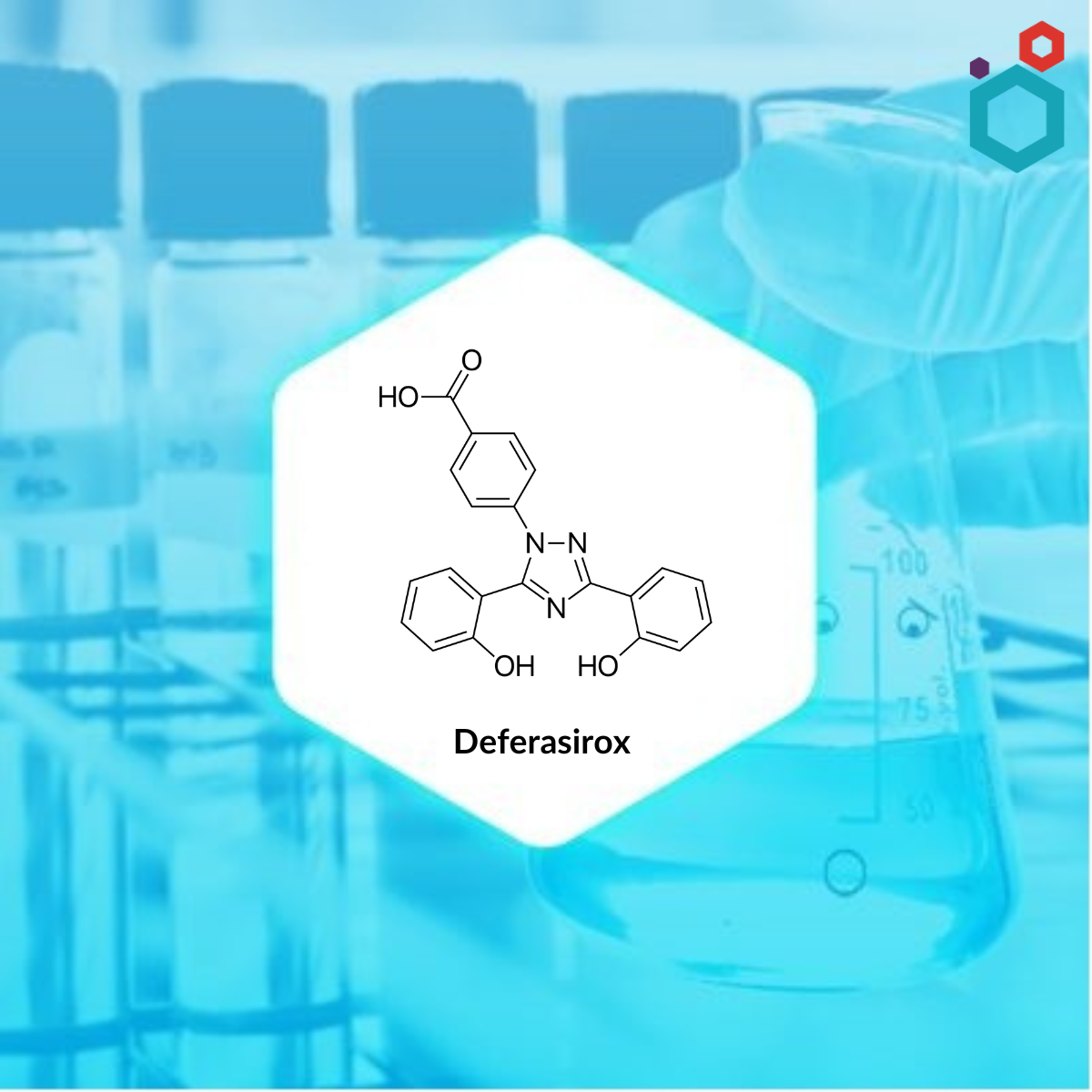
| IUPAC Name | 4-[3,5-bis(2-hydroxyphenyl)-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl]benzoic acid |
| Synonyms | Exjade; Jadenu; Osveral; Déférasirox; Deferasiroxum |
| CAS No | 201530-41-8 |
| Molecular Formula | C21H15N3O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 373.4 g/mol |
| Pubchem CID | 214348 |
Chemical Properties
| SR. No | Criteria | Limit/Specification |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Appearance (Form) | Solid Crystals or Powder |
| 2 | Appearance (Color) | White to slightly yellow |
| 3 | Solubility | Soluble in water (<1 mg/ml at 25° C), DMSO (75 mg/ml at 25° C), ethanol (2 mg/ml at 25° C), methanol, and ethyl acetate |
| 4 | Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
| 5 | Melting Point | 258-263° C |
Mechanism of action
Some forms of blood disorders (such as sickle cell disease, anemia, thalassemia) typically necessitate frequent blood transfusions, which lead to an excess of iron content in the body. It is critical to eliminate excess iron since high amounts of iron can create health concerns (such as heart failure, liver disease, diabetes, and delayed growth in children). Deferasirox serves as an iron chelator. It binds to the iron molecule (Fe 3+) with high affinity in a 2:1 ratio and forms a stable complex, which is then excreted mainly in the stools.
Uses
- Deferasirox is primarily used to reduce chronic iron overload in patients (in adults and children of 2 years of age and older) who are on blood transfusions from a long time for diseases like beta-thalassemia and other chronic anemias.
- It is also used to treat people who have an excessive amount of iron in their bodies due to a genetic blood condition known as non–transfusion-dependent thalassemia (NTDT).
- It is used in patients with elevated liver iron concentration and serum ferritin.
Side effects
The common side effects associated with the use of Deferasirox are-
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Skin rashes
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhea
Serious side effects include-
- Vision problems
- Hearing loss
- Kidney Failure
- Cytopenia
- Bloody or tarry stools
FAQs
Q. What is the difference between Deferasirox and Deferiprone?
Deferasirox and Deferiprone are oral iron-chelating agents used to treat chronic iron overload. However, Deferiprone is less expensive compared to Deferasirox and is superior in controlling or reducing myocardial iron load.
Q. What are the contraindications of using Deferasirox?
Deferasirox may cause fatal nephrotoxicity and is contraindicated for use in patients with renal failure or severe renal impairment. It is also contraindicated in patients suffering from hepatic disease and in those who are on anticoagulant therapy.
Q. What is the half life of Deferasirox?
Deferasirox has a dose-dependent plasma half-life of 12 to 18 hours and can be taken orally once a day after fasting on an empty stomach.
Buy high purity Deferasirox through Macsen Laboratories. For buying, send us an enquiry-
